K29 Di-Ubiquitin VME
activity-based probe for deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) based on K29-linked diUb
Additional information
| Weight | 0.05 kg |
|---|---|
| aliquot size | |
| Applications | Crystallization, Pull down, Purification, Western Blot, Phenotypic protein profiling |
| target | |
| source | |
| shipping | |
| purity | |
| molecular weight | |
| sample preparation | For detailed sample preparation see product sheet. |
| regulatory statement |
€350.00
- Description
- Additional information
- references
Description
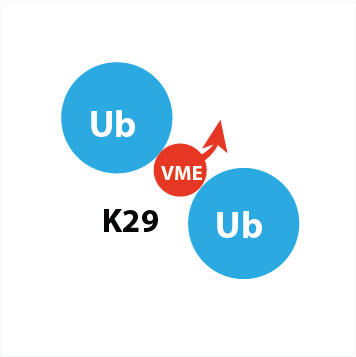
UbiQ-084 is an activity-based probe for deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) based on K29-linked diUb. Here Ly29 has been replaced by a diaminobutyric acid residue equipped with a VME type warhead – the Dab(VME) type of structure is a DUB reactive mimic of the native isopeptidic linked Lys(Gly) residue (Figure 1). Please note that the native distance between the proximal and distal Ub is preserved as much as possible.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.05 kg |
|---|---|
| aliquot size | |
| Applications | Crystallization, Pull down, Purification, Western Blot, Phenotypic protein profiling |
| target | |
| source | |
| shipping | |
| purity | |
| molecular weight | |
| sample preparation | For detailed sample preparation see product sheet. |
| regulatory statement |
Misaghi, S., et al. Structure of the Ubiquitin Hydrolase UCH-L3 Complexed with a Suicide Substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 1512-1520 (2005).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15531586
de Jong, A., et al. Ubiquitin-based probes prepared by total synthesis to profile the activity of deubiquitinating enzymes. ChemBiochem 13, 2251-2258 (2012).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23011887
Altun, M., et al. Activity-based chemical proteomics accelerates inhibitor development for deubiquitylating enzymes. Chem. Biol. 18, 1401-1412 (2011).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22118674
Mulder, M.P., et al. A native chemical ligation handle that enables the synthesis of advanced activity-based probes: diubiquitin as a case study. ChemBiochem 15, 946-949 (2014).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24623714
Haj-Yahya, N., et al. Dehydroalanine-based diubiquitin activity probes. Org. Lett. 16, 540-543 (2014).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24364494
Li, G., et al. Activity-based diubiquitin probes for elucidating the linkage specificity of deubiquitinating enzymes. Chem. Commun. 20, 216-218 (2014).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24225431
Iphöfer, A., et al. Profiling ubiquitin linkage specificities of deubiquitinating enzymes with branched ubiquitin isopeptide probes. Chembiochem 13, 1416-1420 (2012).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22689415
McGouran, J.F., et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme specificity for ubiquitin chain topology profiled by di-ubiquitin activity probes. Chem. Biol. 20, 1447-1455 (2013).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24290882
