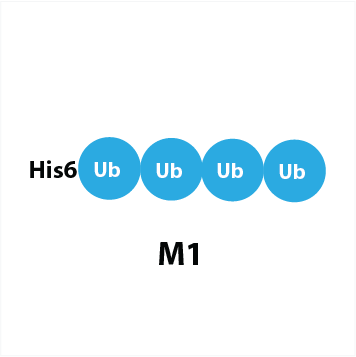
linear His6-tetra-ubiquitin
a linear (i.e. Met1) linked tetra-ubiquitin which is His6 tagged on the N-terminus of the most distal Ub
Additional information
| Weight | 0.05 kg |
|---|---|
| aliquot size | |
| Applications | |
| target | |
| source | |
| shipping | |
| purity | |
| molecular weight | |
| storage | upon arrival, powder at −20°C; solution at −80°C. Please avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles. |
| sample preparation | For detailed sample preparation, please see product sheet. |
| regulatory statement |
€225.00
- Description
- Additional information
- references
Description
UbiQ-366 is linear (i.e. Met1) linked tetra-ubiquitin which is His6 tagged on the N-terminus of the most distal Ub. It can be used as a substrate for proteases that cleave the peptide linkage between two ubiquitin proteins or to investigate mechanism of binding and recognition by proteins that contain ubiquitin-associated domains or ubiquitin-interacting motifs (UIMs). This product was prepared by recombinant expression (E. coli).
Additional information
| Weight | 0.05 kg |
|---|---|
| aliquot size | |
| Applications | |
| target | |
| source | |
| shipping | |
| purity | |
| molecular weight | |
| storage | upon arrival, powder at −20°C; solution at −80°C. Please avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles. |
| sample preparation | For detailed sample preparation, please see product sheet. |
| regulatory statement |
El Oualid, F., et al. Chemical Synthesis of Ubiquitin, Ubiquitin-Based Probes, and Diubiquitin. Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed. 49, 10149-10153 (2010).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21117055
Faesen, A.C., et al. The Differential Modulation of USP Activity by Internal Regulatory Domains, Interactors and Eight Ubiquitin Chain Types. Chem. Biol. 18, 1550-1561 (2011).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22195557
Licchesi, J.D., et al. An ankyrin-repeat ubiquitin-binding domain determines TRABID’s specificity for atypical ubiquitin chains. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 62-71 (2012).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22157957
Walczak, H., et al. Generation and physiological roles of linear ubiquitin chains. BMC Biol. DOI:10.1186/1741-7007-10-23 (2012).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22420778
Keusekotten, K., et al. OTULIN antagonizes LUBAC signaling by specifically hydrolyzing Met1-linked polyubiquitin. Cell 153, 1312-1326 (2013).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23746843
Rivkin, E., et al. The linear ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinase gumby regulates angiogenesis. Nature 498, 318-324 (2013).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23708998
