DUB activity-based probe mix – HA tagged
UbiQ-L06 is a panel of three activity-based probes for deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) (50 μg each).
Additional information
| Weight | 0.01 kg |
|---|---|
| Applications | Crystallization, Pull down, Purification, Western Blot, MS, NMR, Phenotypic protein profiling |
| target | |
| source | |
| shipping | |
| storage | upon arrival, powder at −20°C; solution at −80°C. Avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles. |
| sample preparation | For detailed sample preparation see product sheet. |
| regulatory statement | |
| aliquot size |
€600.00
- Description
- Additional information
- references
Description
UbiQ-L06 is a panel of three activity-based probes for deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) (50 μg each).
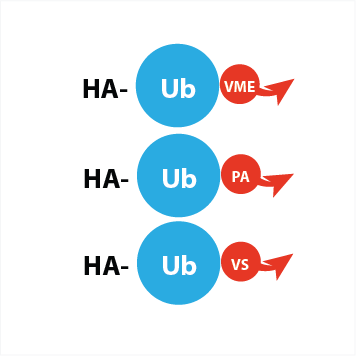
The probes are based on ubiquitin and labeled on the N-terminus with a HA-tag. The HA peptide sequence (YPYDVPDYA) is derived from the influenza hemagglutinin protein and allows for the sensitive identification or purification of DUBs since it is specifically recognized by anti-HA antibodies and anti-HA-agarose. The HA tag is separated from the Ub N-terminus by two 6-aminohexanoic acid (Ahx) linkers for efficient recognition of the tag.
By mixing the three probes, a highly DUB reactive probe mix is obtained that contains the combined reactivity of the PA (propargyl amide), VME (vinyl methyl ester) and VS (vinyl sulfone) electrophiles. As a result the labelling efficiency of the mix is higher than using each probe separately.
| tag | code | |||
| HA | UbiQ-035 | HA-Ahx-Ahx-Ub-VME | ||
| HA | UbiQ-078 | HA-Ahx-Ahx-Ub-PA | ||
| HA | UbiQ-187 | HA-Ahx-Ahx-Ub-VS | ||
Additional information
| Weight | 0.01 kg |
|---|---|
| Applications | Crystallization, Pull down, Purification, Western Blot, MS, NMR, Phenotypic protein profiling |
| target | |
| source | |
| shipping | |
| storage | upon arrival, powder at −20°C; solution at −80°C. Avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles. |
| sample preparation | For detailed sample preparation see product sheet. |
| regulatory statement | |
| aliquot size |
Misaghi, S., et al. Structure of the Ubiquitin Hydrolase UCH-L3 Complexed with a Suicide Substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 1512-1520 (2005).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15531586
de Jong, A., et al. Ubiquitin-based probes prepared by total synthesis to profile the activity of deubiquitinating enzymes. ChemBiochem 13, 2251-2258 (2012).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23011887
Altun, M., et al. Activity-based chemical proteomics accelerates inhibitor development for deubiquitylating enzymes. Chem. Biol. 18, 1401-1412 (2011).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22118674
